Attention: Here be dragons
This is the latest
(unstable) version of this documentation, which may document features
not available in or compatible with released stable versions of Godot.
Checking the stable version of the documentation...
角色动画¶
这是最后一课,我们会使用 Godot 的内置动画工具制作角色的浮动和拍打动画。你会学到如何在编辑器中设计动画,以及如何使用代码让游戏变得活灵活现。

我们将会开始介绍动画编辑器的使用。
动画编辑器的使用¶
该引擎自带的工具可以在编辑器中编写动画。然后你可以在运行时使用代码来播放和控制它们。
Open the player scene, select the Player node, and add an AnimationPlayer node.
动画停靠面板就会出现在底部面板中。
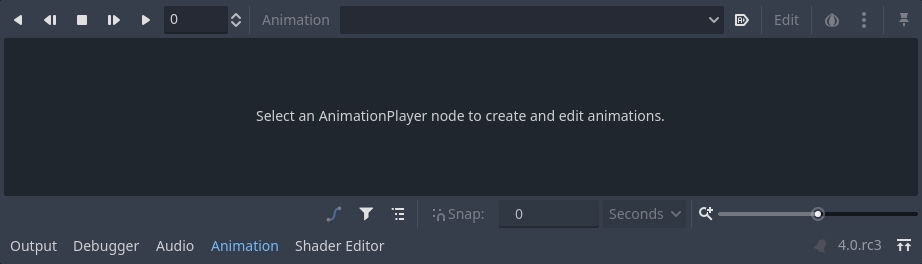
它的特点是顶部有一个工具栏和动画下拉菜单,中间有一个轨道编辑器,目前是空的,底部有过滤、捕捉和缩放选项。
让我们来创建一个动画。请点击动画 -> 新建。
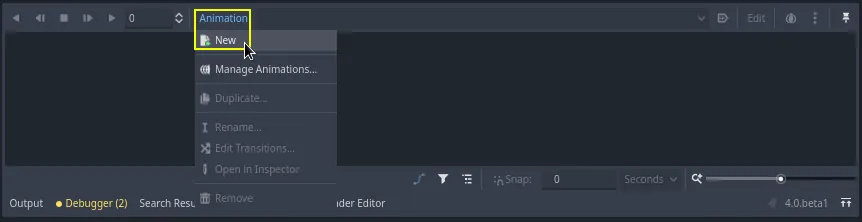
将动画命名为“float”(漂浮)。
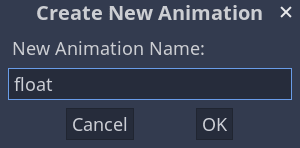
Once you've created the animation, the timeline appears with numbers representing time in seconds.

我们希望让这个动画在游戏开始时自动开始播放,而且还应该循环播放。
要实现这个需求,可以单击动画工具栏上对应的“A+”图标和循环箭头。
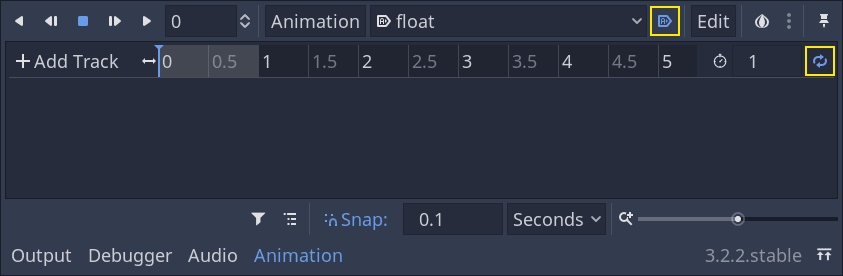
你还可以单击右上角的图钉图标,将动画编辑器进行固定。这样它就不会在你点击视口取消选择节点时折叠。
![]()
在面板右上角将动画的时长设为 1.2 秒。
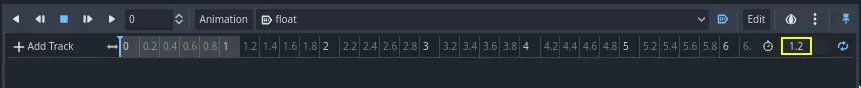
您应该看到灰色带子变宽了一点。它显示动画的开始和结束,垂直蓝线是您的时间光标。
单击并拖拽右下角的滑动条,即可将时间线进行缩放。
漂浮动画¶
使用动画播放器节点,你可以对所需任意数量的节点的大多数属性做动画。请注意检查器中属性旁的钥匙图标。在上面单击就可以创建一个关键帧,即对应属性的一对时间与值。关键帧会被插入到时间线上的时间光标处。
Let's insert our first keys. Here, we will animate both the position and the
rotation of the Character node.
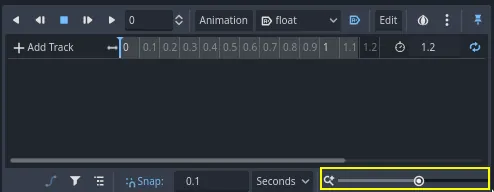
Select the Character and in the Inspector expand the Transform section. Click the key icon next to Position, and Rotation.
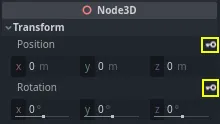
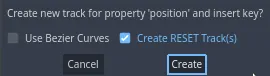
For this tutorial, just create RESET Track(s) which is the default choice
编辑器中会出现两个轨道,各有一个代表关键帧的菱形图标。
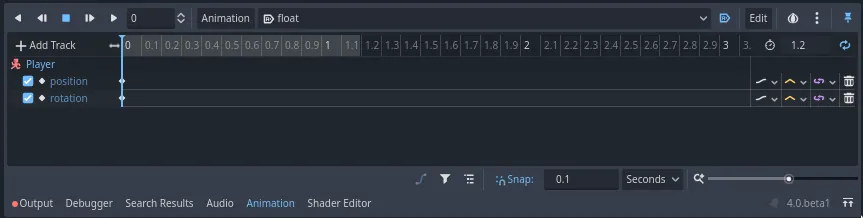
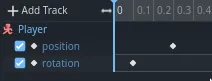
You can click and drag on the diamonds to move them in time. Move the
position key to 0.2 seconds and the rotation key to 0.1 seconds.
Move the time cursor to 0.5 seconds by clicking and dragging on the gray
timeline.
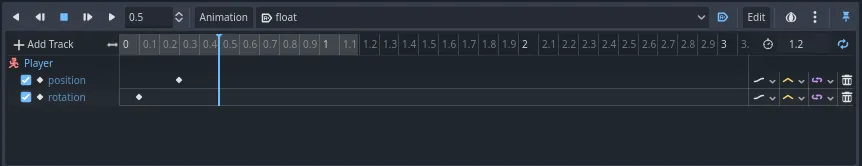
In the Inspector, set the Position's Y axis to 0.65 meters and the Rotation' X axis to 8.
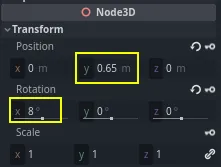
Create a keyframe for both properties
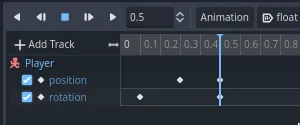
Now, move the position keyframe to 0.7
seconds by dragging it on the timeline.
备注
关于动画原理的讲解已经超出了本教程的范围。请注意,您不想均匀地分配时间和空间。取而代之的是,动画师使用时间和间隔,这两个核心动画原则。您希望让它们存在一定的偏移,在角色的运动中产生对比,以使他们感觉生动。
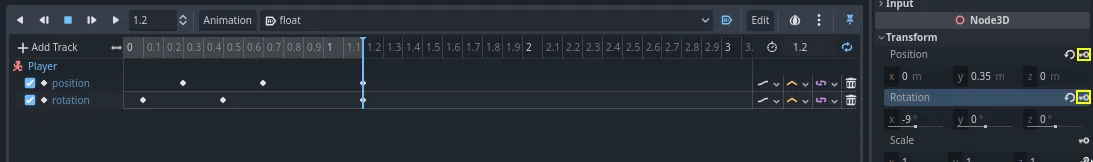
Move the time cursor to the end of the animation, at 1.2 seconds. Set the Y
position to about 0.35 and the X rotation to -9 degrees. Once again,
create a key for both properties.
单击播放按钮或者按 Shift + D 即可预览结果。单击停止按钮或者按 S 即可停止播放。
您可以看到引擎在关键帧之间插值以生成连续动画。不过目前,这个动作感觉非常机器人化。这是因为默认插值是线性的,导致持续的过渡,这与现实世界中生物的移动方式不同。
我们可以使用缓动曲线来控制关键帧之间的过渡。
单击并拖拽,框选时间线上的前两个关键帧。
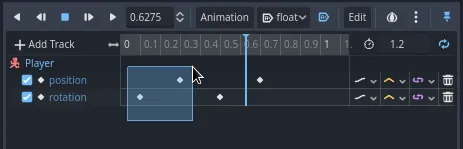
可以在检查器中同时编辑这两个关键帧的属性,其中就有一个属性叫做 Easing(缓动)。
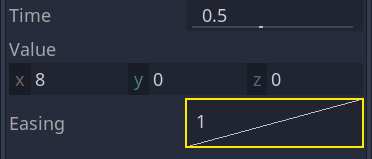
单击并拖动曲线,把它往左拉。这样就会让他实现缓出,也就是说,一开始变得快,然后时间光标越接近下一个关键帧就变得越慢。
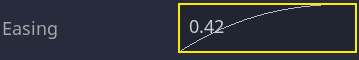
再次播放动画以查看差异。前半部分应该已经感觉有点弹性了。
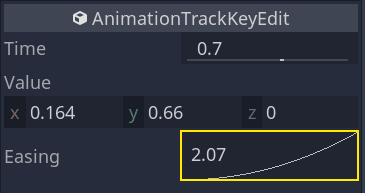
将缓动效果应用于旋转轨迹中的第二个关键帧。
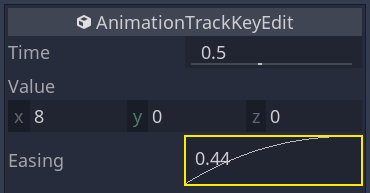
Do the opposite for the second position keyframe, dragging it to the right.
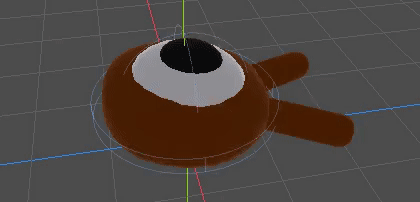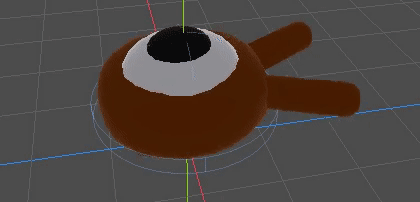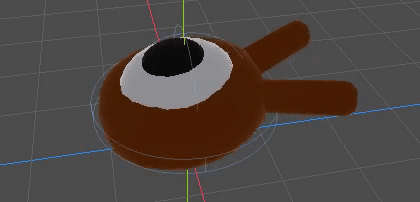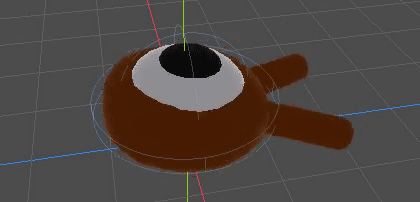
你的动画应该类似这样。
备注
每一帧,动画都会去更新被动画的节点的属性,覆盖掉初始值。如果我们直接对 Player 节点做动画,就没法使用代码来移动它了。这就是 Pivot 节点的用处:尽管我们为 Character 做了动画,我们还是可以在此动画之上,再通过代码来移动并旋转 Pivot。
如果你运行游戏,玩家的生物就会漂浮起来!
If the creature is a little too close to the floor, you can move the Pivot up
to offset it.
使用代码控制动画¶
我们可以使用代码来根据玩家的输入控制动画的播放。让我们在角色移动时修改动画的速度吧。
Open the Player's script by clicking the script icon next to it.
![]()
在 _physics_process() 中检查 direction 向量的那一行之后添加如下代码。
func _physics_process(delta):
#...
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
#...
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = 4
else:
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = 1
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
// ...
if (direction != Vector3.Zero)
{
// ...
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").SpeedScale = 4;
}
else
{
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").SpeedScale = 1;
}
}
这段代码的作用是让玩家在移动时将播放速度乘以 4。在停止移动时将其恢复原状。
We mentioned that the Pivot could layer transforms on top of the animation. We
can make the character arc when jumping using the following line of code. Add it
at the end of _physics_process().
func _physics_process(delta):
#...
$Pivot.rotation.x = PI / 6 * velocity.y / jump_impulse
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
// ...
var pivot = GetNode<Node3D>("Pivot");
pivot.Rotation = new Vector3(Mathf.Pi / 6.0f * Velocity.Y / JumpImpulse, pivot.Rotation.Y, pivot.Rotation.Z);
}
为小怪制作动画¶
在 Godot 中还有一个很好的动画技巧:只要你使用类似的节点结构,你就可以把它们复制到不同的场景中。
For example, both the Mob and the Player scenes have a Pivot and a
Character node, so we can reuse animations between them.
Open the Player scene, select the AnimationPlayer node and open the "float"
animation. Next, click on Animation > Copy. Then open mob.tscn,
create an AnimationPlayer child node and select it. Click Animation > Paste
and make sure that the button with an "A+" icon (Autoplay on Load) and the
looping arrows (Animation looping) are also turned on in the animation editor
in the bottom panel. That's it; all monsters will now play the float animation.
我们可以根据生物的 random_speed 来更改播放速度。打开 Mob 的脚本,在 initialize() 函数的末尾添加下面这行代码。
func initialize(start_position, player_position):
#...
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = random_speed / min_speed
public void Initialize(Vector3 startPosition, Vector3 playerPosition)
{
// ...
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").SpeedScale = randomSpeed / MinSpeed;
}
这样,你就完成了你第一个完整 3D 游戏的编码。
恭喜!
在下一部分,我们将快速复习已学到的内容,并为你提供一些继续学习的链接。不过现在,这里是完整的 Player.gd 和 Mob.gd,你可以用它们来校对你的代码。
这是 Player 脚本。
extends CharacterBody3D
signal hit
# How fast the player moves in meters per second.
@export var speed = 14
# The downward acceleration while in the air, in meters per second squared.
@export var fall_acceleration = 75
# Vertical impulse applied to the character upon jumping in meters per second.
@export var jump_impulse = 20
# Vertical impulse applied to the character upon bouncing over a mob
# in meters per second.
@export var bounce_impulse = 16
var target_velocity = Vector3.ZERO
func _physics_process(delta):
# We create a local variable to store the input direction
var direction = Vector3.ZERO
# We check for each move input and update the direction accordingly
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_right"):
direction.x = direction.x + 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_left"):
direction.x = direction.x - 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_back"):
# Notice how we are working with the vector's x and z axes.
# In 3D, the XZ plane is the ground plane.
direction.z = direction.z + 1
if Input.is_action_pressed("move_forward"):
direction.z = direction.z - 1
# Prevent diagonal movement being very fast
if direction != Vector3.ZERO:
direction = direction.normalized()
$Pivot.look_at(position + direction,Vector3.UP)
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = 4
else:
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = 1
# Ground Velocity
target_velocity.x = direction.x * speed
target_velocity.z = direction.z * speed
# Vertical Velocity
if not is_on_floor(): # If in the air, fall towards the floor
target_velocity.y = target_velocity.y - (fall_acceleration * delta)
# Jumping.
if is_on_floor() and Input.is_action_just_pressed("jump"):
target_velocity.y = jump_impulse
# Iterate through all collisions that occurred this frame
# in C this would be for(int i = 0; i < collisions.Count; i++)
for index in range(get_slide_collision_count()):
# We get one of the collisions with the player
var collision = get_slide_collision(index)
# If the collision is with ground
if (collision.get_collider() == null):
continue
# If the collider is with a mob
if collision.get_collider().is_in_group("mob"):
var mob = collision.get_collider()
# we check that we are hitting it from above.
if Vector3.UP.dot(collision.get_normal()) > 0.1:
# If so, we squash it and bounce.
mob.squash()
target_velocity.y = bounce_impulse
# Moving the Character
velocity = target_velocity
move_and_slide()
$Pivot.rotation.x = PI / 6 * velocity.y / jump_impulse
# And this function at the bottom.
func die():
hit.emit()
queue_free()
func _on_mob_detector_body_entered(body):
die()
using Godot;
public partial class Player : CharacterBody3D
{
// Emitted when the player was hit by a mob.
[Signal]
public delegate void HitEventHandler();
// How fast the player moves in meters per second.
[Export]
public int Speed { get; set; } = 14;
// The downward acceleration when in the air, in meters per second squared.
[Export]
public int FallAcceleration { get; set; } = 75;
// Vertical impulse applied to the character upon jumping in meters per second.
[Export]
public int JumpImpulse { get; set; } = 20;
// Vertical impulse applied to the character upon bouncing over a mob in meters per second.
[Export]
public int BounceImpulse { get; set; } = 16;
private Vector3 _targetVelocity = Vector3.Zero;
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
// We create a local variable to store the input direction.
var direction = Vector3.Zero;
// We check for each move input and update the direction accordingly.
if (Input.IsActionPressed("move_right"))
{
direction.X += 1.0f;
}
if (Input.IsActionPressed("move_left"))
{
direction.X -= 1.0f;
}
if (Input.IsActionPressed("move_back"))
{
// Notice how we are working with the vector's X and Z axes.
// In 3D, the XZ plane is the ground plane.
direction.Z += 1.0f;
}
if (Input.IsActionPressed("move_forward"))
{
direction.Z -= 1.0f;
}
// Prevent diagonal movement being very fast.
if (direction != Vector3.Zero)
{
direction = direction.Normalized();
GetNode<Node3D>("Pivot").LookAt(Position + direction, Vector3.Up);
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").PlaybackSpeed = 4;
}
else
{
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").PlaybackSpeed = 1;
}
// Ground velocity
_targetVelocity.X = direction.X * Speed;
_targetVelocity.Z = direction.Z * Speed;
// Vertical velocity
if (!IsOnFloor())
{
_targetVelocity.Y -= FallAcceleration * (float)delta;
}
// Jumping.
if (IsOnFloor() && Input.IsActionJustPressed("jump"))
{
_targetVelocity.y += JumpImpulse;
}
// Iterate through all collisions that occurred this frame.
for (int index = 0; index < GetSlideCollisionCount(); index++)
{
// We get one of the collisions with the player.
KinematicCollision3D collision = GetSlideCollision(index);
// If the collision is with a mob.
if (collision.GetCollider() is Mob mob)
{
// We check that we are hitting it from above.
if (Vector3.Up.Dot(collision.GetNormal()) > 0.1f)
{
// If so, we squash it and bounce.
mob.Squash();
_targetVelocity.Y = BounceImpulse;
}
}
}
// Moving the character
Velocity = _targetVelocity;
MoveAndSlide();
var pivot = GetNode<Node3D>("Pivot");
pivot.Rotation = new Vector3(Mathf.Pi / 6.0f * Velocity.Y / JumpImpulse, pivot.Rotation.Y, pivot.Rotation.Z);
}
private void Die()
{
EmitSignal(SignalName.Hit);
QueueFree();
}
private void OnMobDetectorBodyEntered(Node body)
{
Die();
}
}
这是 Mob 的脚本。
extends CharacterBody3D
# Minimum speed of the mob in meters per second.
@export var min_speed = 10
# Maximum speed of the mob in meters per second.
@export var max_speed = 18
# Emitted when the player jumped on the mob
signal squashed
func _physics_process(_delta):
move_and_slide()
# This function will be called from the Main scene.
func initialize(start_position, player_position):
# We position the mob by placing it at start_position
# and rotate it towards player_position, so it looks at the player.
look_at_from_position(start_position, player_position, Vector3.UP)
# Rotate this mob randomly within range of -90 and +90 degrees,
# so that it doesn't move directly towards the player.
rotate_y(randf_range(-PI / 4, PI / 4))
# We calculate a random speed (integer)
var random_speed = randi_range(min_speed, max_speed)
# We calculate a forward velocity that represents the speed.
velocity = Vector3.FORWARD * random_speed
# We then rotate the velocity vector based on the mob's Y rotation
# in order to move in the direction the mob is looking.
velocity = velocity.rotated(Vector3.UP, rotation.y)
$AnimationPlayer.speed_scale = random_speed / min_speed
func _on_visible_on_screen_notifier_3d_screen_exited():
queue_free()
func squash():
squashed.emit()
queue_free() # Destroy this node
using Godot;
public partial class Mob : CharacterBody3D
{
// Emitted when the played jumped on the mob.
[Signal]
public delegate void SquashedEventHandler();
// Minimum speed of the mob in meters per second
[Export]
public int MinSpeed { get; set; } = 10;
// Maximum speed of the mob in meters per second
[Export]
public int MaxSpeed { get; set; } = 18;
public override void _PhysicsProcess(double delta)
{
MoveAndSlide();
}
// This function will be called from the Main scene.
public void Initialize(Vector3 startPosition, Vector3 playerPosition)
{
// We position the mob by placing it at startPosition
// and rotate it towards playerPosition, so it looks at the player.
LookAtFromPosition(startPosition, playerPosition, Vector3.Up);
// Rotate this mob randomly within range of -90 and +90 degrees,
// so that it doesn't move directly towards the player.
RotateY((float)GD.RandRange(-Mathf.Pi / 4.0, Mathf.Pi / 4.0));
// We calculate a random speed (integer).
int randomSpeed = GD.RandRange(MinSpeed, MaxSpeed);
// We calculate a forward velocity that represents the speed.
Velocity = Vector3.Forward * randomSpeed;
// We then rotate the velocity vector based on the mob's Y rotation
// in order to move in the direction the mob is looking.
Velocity = Velocity.Rotated(Vector3.Up, Rotation.Y);
GetNode<AnimationPlayer>("AnimationPlayer").SpeedScale = randomSpeed / MinSpeed;
}
public void Squash()
{
EmitSignal(SignalName.Squashed);
QueueFree(); // Destroy this node
}
private void OnVisibilityNotifierScreenExited()
{
QueueFree();
}
}